Motility Made Easy
May 19, 2023CPOA Highlights and Review Course
June 20, 2023Visual Field Testing Manual and Automated
Associated Courses
$45.00
This course is for educational purposes and will result in 3 CEs. It is intended for beginning, intermediate, and advanced levels.
After completing this section the student should be able to do the following:
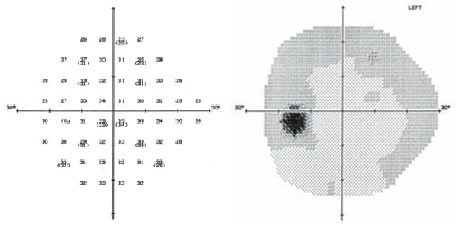
- Define Visual Field
- List the limits on a normal visual field superiorly, nasally, inferiorly, and temporally
- Define the following visual perimetry terms: Stimulus, isopter, scotoma, relative, absolute, kinetic, and static
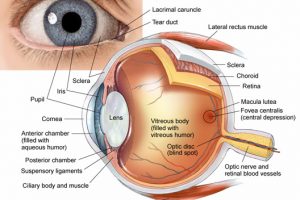
- Describe the island of vision
- Describe the 2 methods of stimulus presentation used for Visual field perimetry
- List the 5 types of visual field (perimetry) testing
- Describe how to perform confrontational field testing
- Identify which types of perimetry are done manually and which types are automated
- Describe how to use the static and kinetic methods on a Goldmann perimeter
- Describe how to map a visual field on the tangent screen
- Identify where the physiological blind spot falls
- Identify one aspect of the tangent screen that helps detect malingering
- Compare suprathreshold testing vs. threshold testing
- Describe normal amsler grid versus abnormal amsler grid findings
- Find the appropriate lens needed for a patient for a Goldmann visual field given the refractive error and age of the patient
- Describe the patient instructions for performing a Goldmann perimeter test
- Describe how to plot isopters on a Goldmann perimeter
- Identify 4 automated perimeter machines
- Describe the differences between full threshold, SITA, & Fastpac on the Humphrey Analyzer
- List tests that could be done on the Humphrey Field Analyzer that might be beneficial for glaucoma patients.
- Compare SWAP testing with Standard automated perimeter testing
- List 4 tests that can be done on most Humphrey Field Analyzers
- Describe the stimulus color and size variations available on a Humphrey Field Analyzer
- Describe the stimulus color and size variations available on a Humphrey Field Analyzer
- Describe when a patient may not need a corrective lens placed in front of his eye when undergoing Humphrey Field testing
- Compare and contrast false positive errors, false negative errors and fixation losses
- List 5 conditions or disease that might indicate visual field testing is necessary
- Identify common visual field abnormalities found in patients with Glaucoma
- Identify common visual field abnormalities found in patients with pituitary tumors
- Identify common visual field abnormalities found in patients with brain tumors
- Describe how gaze tracking helps with automated visual field results
- Identify normal versus abnormal dB numbers on automated field printouts
- Identify normal versus abnormal results on grayscale print outs
- Identify the limits in decibels on the Humphrey Field Analyzer
- List 6 sources of operator error in field testing
- List 2 extra sources of operator error on Kinetic field testing
- List 3 sources of patient error on field testing
- List 3 sources of machine induced error on field testing
This course should take approximately three hours to complete.
You must correctly answer at least 21 of the 30 questions on the open book post test to earn credit. If you do not successfully pass the post test the first time you may try again at no expense to you. Successful completion of the post-test is required to earn CE credit.
This course should take approximately 2 hours to complete.
This course has been approved by the AOA Commission on Paraoptometric Certification (CPC) for continuing education credit for use toward paraoptometric certification renewal.
Related products
-
Photography Basics
$15.00 -
Basic Anatomy
$15.00 -
Glaucoma Overview
$15.00